What is the difference between adult acne and teen acne?

Adult vs. Teen Acne: Understanding Causes and Treatments
While acne is most commonly associated with adolescence, it doesn’t always disappear at the end of puberty. Studies show that 50% of women in their 20s, 25% in their 30s, and 20% of men continue to struggle with acne beyond their teenage years. Like teens, adults with acne often face negative effects on self-esteem, social interactions, and even workplace experiences. Some research suggests that acne may impact adults’ quality of life more severely, as adult skin regenerates more slowly, leading to more lasting scars.
Adult acne and teen acne differ in causes, locations, and treatment approaches. Here’s a closer look at the factors involved and effective treatments for both.
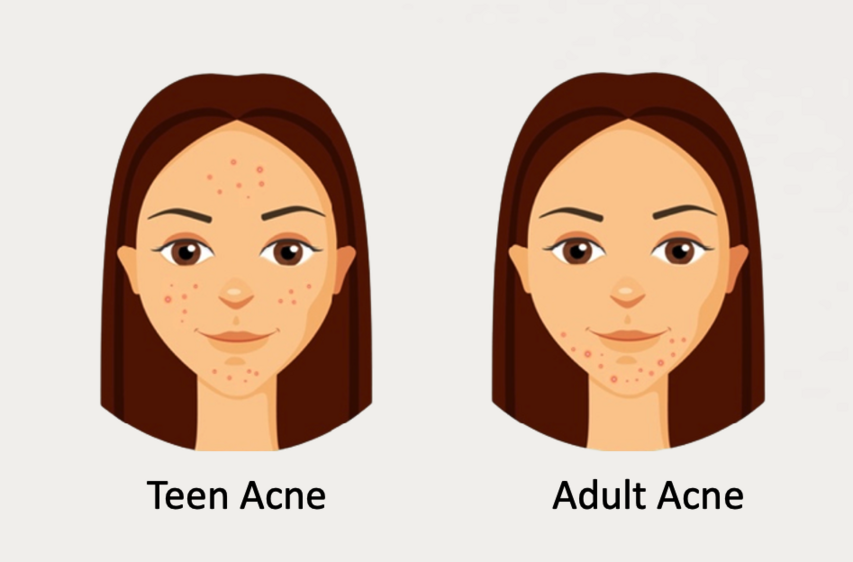
What Causes Teen and Adult Acne?
During puberty, increased levels of androgens, like testosterone, enlarge sebaceous (oil) glands, leading to oilier skin. When excess oil mixes with dead skin cells, it clogs pores, providing an environment where acne-causing bacteria can thrive, leading to inflammation and breakouts.
For adults, hormonal fluctuations often play a significant role. Many women experience acne flare-ups before menstruation, during pregnancy, or due to conditions like polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS). Additional factors include certain medications (e.g., steroids, lithium), skin picking, and the use of heavy or comedogenic makeup products.
Both teens and adults may experience acne due to:
- High-glycemic foods like sweets and processed carbs
- Dairy, particularly cow’s milk
- Incorrect skincare, such as overuse of oil-based products or overly frequent washing
Location Differentiation: Teen acne often appears on the forehead and cheeks, while adult acne typically affects the lower face, including the mouth, chin, and jawline.
Treating Teen vs. Adult Acne
Teenage skin is usually oilier, so it can tolerate stronger, drying acne treatments. Adults, however, benefit from milder treatments paired with oil-free moisturizers to avoid excessive dryness.
Best Treatments for Adult Acne
-
Comprehensive Routine: An effective regimen includes preventive steps like a balanced diet, appropriate makeup, a mild cleanser, an oil-free moisturizer, and a customized night cream.
-
Diet: Low-glycemic foods, such as fresh fruits, nuts, wild fish, and hormone-free meat, can help reduce breakouts by lowering inflammation.
-
Topical Treatments:
- Blackheads & Whiteheads: Salicylic acid is effective for adults with dry skin, as it removes excess oil and exfoliates dead cells without overly drying the skin.
- Inflamed Pimples: Benzoyl peroxide (2.5%) kills acne-causing bacteria and reduces inflammation. While topical antibiotics like clindamycin and erythromycin are also effective, they should not be used alone due to potential bacterial resistance.
- Retinoids: Retinoids encourage cell turnover, helping prevent clogged pores and smooth skin texture. Over-the-counter retinol products at 0.25% to 0.5% are ideal for adults with sensitive skin, avoiding the dryness of stronger prescriptions like Adapalene or Tazarotene.
-
Hormonal Acne Treatments: Birth control pills and spironolactone are common options for balancing hormones in adult women. For those preferring natural options, DIM supplements (containing extracts from vegetables like broccoli and spinach) help balance hormones and reduce breakouts.
-
Under-the-Skin Pimples: Painful cystic acne common in hormonal breakouts can benefit from a combined approach: diet, topical treatment, hormone-balancing supplements, and sometimes oral antibiotics or spironolactone. Severe cases may require Accutane or professional advice.
FAQ Summary
-
Differences in Causes: Teen acne is triggered by hormone-driven oil production, while adult acne is influenced by hormonal fluctuations, lifestyle factors, and sometimes chronic conditions.
-
Treatment Approach: Teens can handle stronger, oil-controlling products, while adults typically need milder, moisturizing formulas to avoid drying their skin.
-
Effective Adult Acne Regimens: Combine preventative care, a proper diet, and tailored topical treatments.
-
Best Diet for Adult Acne: Low-glycemic foods and hormone-free proteins help reduce inflammation.
-
Key Medications for Adult Acne: Salicylic acid for blackheads, benzoyl peroxide for inflamed pimples, and gentle retinoids for cell turnover work well for sensitive adult skin.
-
Treatment for Cystic Acne: Hormone-balancing supplements, oral antibiotics, and medications like spironolactone can support topical treatments for more severe cases.
Adult acne can be persistent, but with the right approach, you can manage it effectively and reduce its impact on your skin and confidence. For severe or persistent acne, consult a dermatologist to customize a treatment plan based on your unique skin needs.
Shop:
Retinol for adult acne
Hormone balancing supplements (DIM) for adult acne
To find the right acne treatments for your unique skin, take the free skin assessment by clicking here.



