The best hyperpigmentation treatment for black skin

Hyperpigmentation, commonly known as "dark spots," occurs when patches of skin darken due to excess melanin—our skin's natural pigment. While it can affect any skin tone, it’s more common in people with darker skin tones, especially Black skin, due to higher melanin levels and a tendency for increased melanin production in response to external triggers. Here’s a guide to understanding and treating hyperpigmentation in Black skin safely and effectively.
Causes of Hyperpigmentation
-
Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): PIH occurs after skin trauma or inflammation, such as acne, eczema, or psoriasis, causing pink, red, or dark brown spots. PIH is common in all skin tones but particularly impacts those with darker skin.
-
Sun Damage: Overexposure to sunlight triggers melanin production, resulting in sunspots, which often darken with continued sun exposure. They appear mainly on areas with high sun exposure, such as the face, neck, and hands.
-
Melasma: Melasma is often triggered by hormonal fluctuations from pregnancy or birth control and typically appears on the cheeks, sides of the face, forehead, and upper lip.
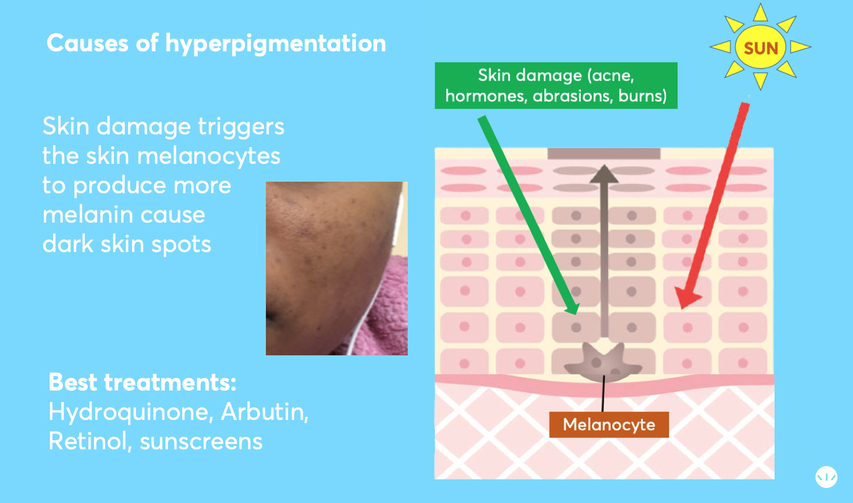
Why Extra Caution is Needed for Black Skin
People with darker skin must be careful with hyperpigmentation treatments, as incorrect products or concentrations can cause irritation or even worsen discoloration. Fortunately, some well-researched ingredients effectively treat hyperpigmentation in darker skin tones.
Best Ingredients for Treating Hyperpigmentation in Black Skin
Certain dermatologist-approved ingredients can help reduce dark spots safely. These ingredients are even more effective and gentler when combined with anti-inflammatory agents.
- Arbutin: A plant-derived compound that inhibits melanin production without damaging melanocytes, especially when combined with antioxidants and other supportive ingredients.
- Bearberry Extract: Known as one of the best plant-based lighteners, it contains antioxidants and anti-inflammatory agents that protect against UV damage and reduce existing pigmentation.
- Indian Gooseberry Extract: A rich source of vitamin C, it helps brighten skin and reduce hyperpigmentation.
- Aloe Vera Leaf Extract: Provides hydration and soothes the skin with antioxidant properties.
- Glycolic Acid (AHA): This exfoliator increases ingredient penetration and accelerates visible results by gently removing dead skin cells.
- Salicylic Acid (BHA): Helps exfoliate, brighten, and enhance other dark-spot treatments' effectiveness.
- Retinyl Palmitate: A form of retinol that promotes cell turnover and reduces melanin accumulation, improving both dark spots and skin elasticity.
- Vitamin E: Protects the skin’s barrier and prevents free-radical damage, promoting a balanced, healthy complexion.
Ingredients to Use with Caution
- Kojic Acid: Though it reduces pigmentation, it may cause irritation in some users and is generally less effective than other options.
- Azelaic Acid: It has mild skin-brightening effects but is typically less potent for hyperpigmentation.
Top Dark Spot Treatments for Black Skin
There are several safe options to treat hyperpigmentation. One trusted option is MDacne's Advanced Dark Spot Remover, designed by dermatologists for sensitive, acne-prone skin. Inspired by the Kligman Formula but without hydroquinone, this formula combines effective, plant-based brighteners with proven ingredients to treat hyperpigmentation gently and effectively.
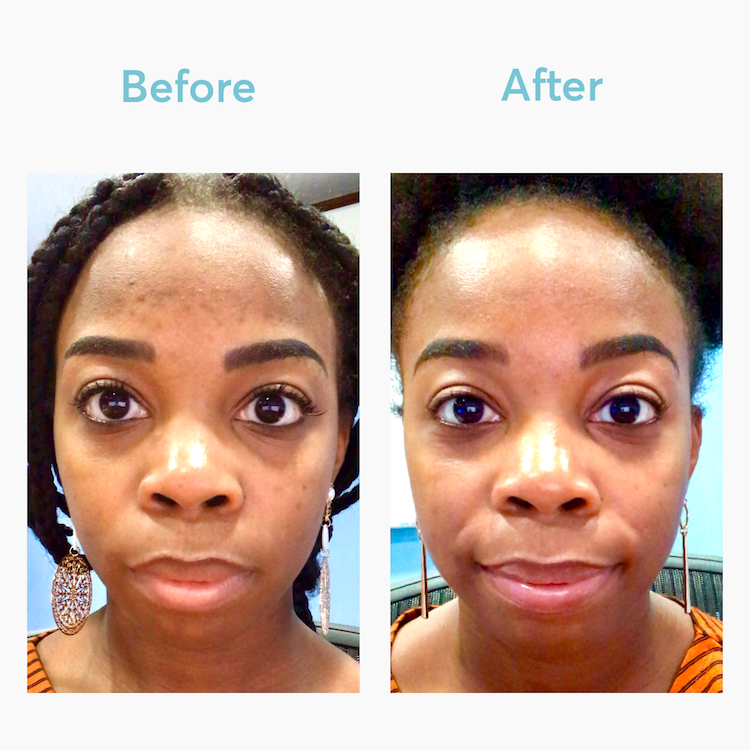

In-Office Treatments for Persistent Hyperpigmentation
If at-home treatments aren’t enough or you need faster results, consider the following:
- Microdermabrasion: Removes the skin’s top layer to improve superficial pigmentation but may not address deeper pigment issues.
- Chemical Peels: Mild peels, like glycolic or salicylic acid, are safer for dark skin. TCA peels are typically avoided due to the risk of hypopigmentation.
- Laser or IPL Treatments: These may reduce dark spots but can increase hypopigmentation risks in Black skin.
Can Diet Help with Hyperpigmentation?
While diet alone won’t remove existing dark spots, anti-inflammatory foods may help reduce acne and support an overall healthier complexion, indirectly benefiting PIH management.
- Green Tea: Contains antioxidants that combat skin inflammation.
- Leafy Greens: High in vitamin C, which helps defend against free radicals.
- Berries: Rich in vitamins C and E for skin healing.
- Omega-3-Rich Fish: Anti-inflammatory, helping balance skin health.
- Healthy Fats: Found in olive oil, avocados, and nuts, they keep the skin hydrated and reduce dryness-related inflammation.
By choosing the right products and nourishing your body with skin-boosting foods, you can achieve a balanced approach to treating hyperpigmentation safely and effectively.
References:
- Davis EC, Callender VD. Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: a review of the epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment options in skin of color. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2010;3(7):20-31. PMID: 20725545.
- Sarkar R, Garg VK, Mysore V. Melasma update. Indian Dermatol Online J. 2014;5(4):426-435.
- Grimes PE. Melasma. Etiologic and therapeutic considerations. Arch Dermatol. 1995;131(12):1453-1457.
- Draelos ZD. Skin lightening preparations and the hydroquinone controversy. Dermatol Ther. 2007;20(5):308-313.
- Alexis AF, Blackcloud P. Chemical peels and microdermabrasion for postinflammatory hyperpigmentation and acne scarring in skin of color. Semin Cutan Med Surg. 2012;31(2):87-92.
To find the right acne treatments for your unique skin, take the free skin assessment by clicking here.



