Rosacea: best treatments according to dermatologists

Understanding Rosacea: Causes, Symptoms, and Effective Treatments
Also known as acne rosacea, rosacea is a common skin condition affecting over 415 million people worldwide and 16 million in the United States. Although typically seen in adults between 30 and 50, it can develop at any age. While there is no cure for rosacea, its symptoms can be effectively managed with proper care and lifestyle adjustments.
Key Symptoms of Rosacea
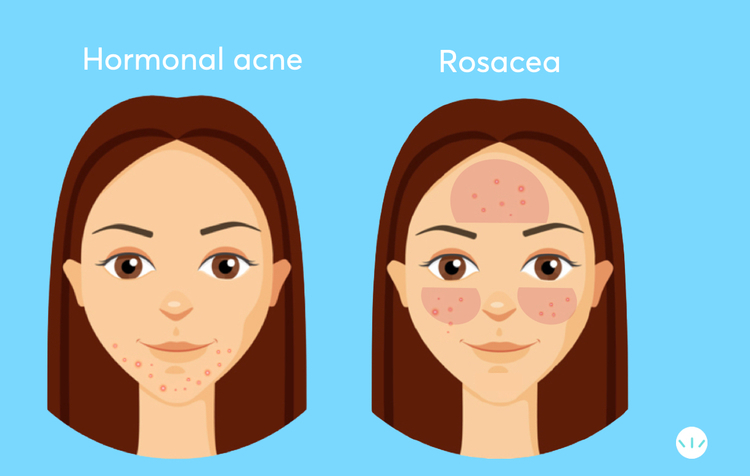
Rosacea is characterized by persistent flushing and redness, especially in the central face. Small, visible blood vessels may appear on the cheeks and nose, along with swollen red bumps that resemble acne but do not form typical comedones and generally do not affect the neck, chest, or back. In moderate to severe cases, rosacea can also cause ocular symptoms, such as dry, irritated eyes and swollen, red eyelids (ocular rosacea).
Rosacea symptoms may fluctuate over time, but treatment is essential to prevent redness and swelling from becoming permanent.
Causes of Rosacea
The exact cause of rosacea remains unclear, but dermatologists suspect a combination of genetic and environmental factors. One theory suggests a link to Demodex folliculorum, a normally harmless skin mite. Research indicates that people with rosacea have significantly higher Demodex mite populations than those without. A study conducted on 1066 participants with acne rosacea lists the most common causes:
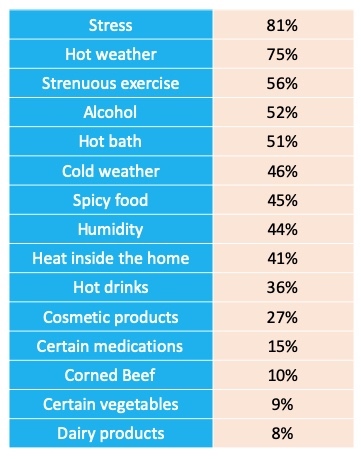
Common Rosacea Triggers:
- Stress
- Alcohol
- Extreme temperatures (hot or cold)
- Spicy foods
- Helicobacter pylori (a type of intestinal bacteria)
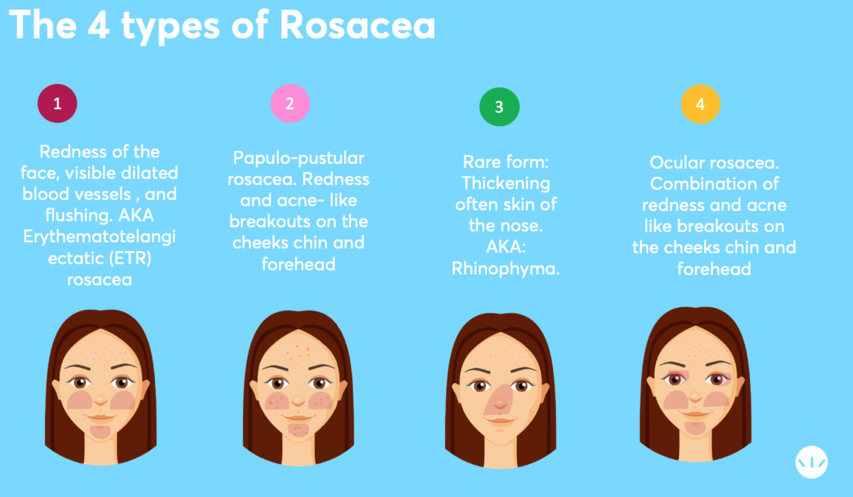
Types of Rosacea
The American Academy of Dermatology (AAD) categorizes rosacea into five types:
- Erythematotelangiectatic Rosacea: Characterized by persistent redness, frequent flushing, and visible blood vessels.
- Papulopustular Rosacea: Involves redness, flushing, and acne-like papules and pustules.
- Phymatous Rosacea: The most severe form, resulting in thickened skin, especially on the nose and cheeks.
- Ocular Rosacea: Affects the eyes, leading to redness, irritation, and swollen eyelids.
- Steroid-Induced Rosacea: Caused by prolonged use of strong steroid creams for conditions like eczema or vitiligo.
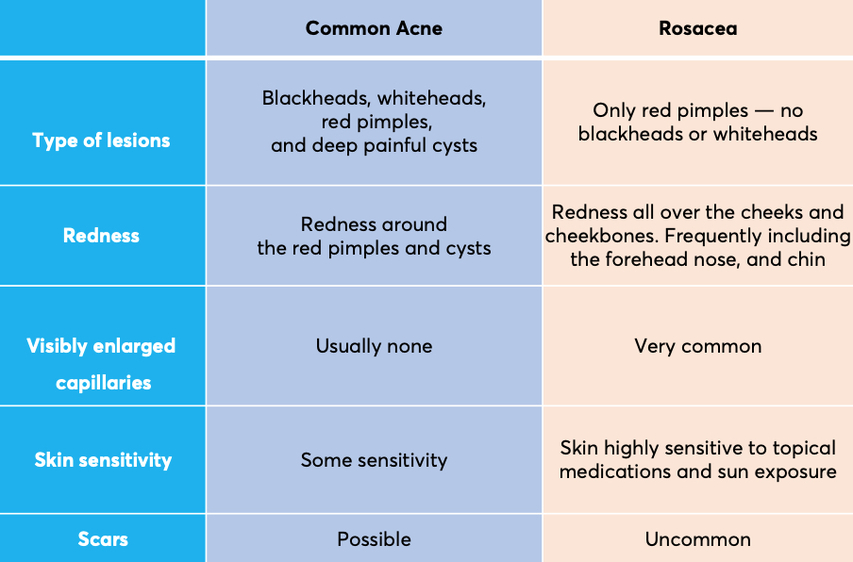
Differences Between Acne Vulgaris and Acne Rosacea
While acne vulgaris and rosacea may look similar, they differ significantly in origin and appearance. Acne vulgaris commonly includes blackheads and whiteheads and can appear on various parts of the body, while rosacea-related bumps are concentrated on the face and typically lack comedones.
Effective Rosacea Treatments
A consistent skincare routine is essential for managing rosacea. The ideal products for rosacea-prone skin are non-irritating and support hydration without clogging pores. Here’s a guide to choosing ingredients that soothe rather than aggravate rosacea:
Topical Ingredients for Rosacea
- Benzoyl Peroxide (BPO): In low doses (around 2.5%), BPO can reduce inflammation without over-drying. Some formulations include aloe vera or other plant extracts to further reduce irritation.
- Niacinamide: This ingredient strengthens the skin barrier, offering anti-inflammatory effects. Niacinamide also boosts ceramide and collagen production, helping to reduce redness and improve skin texture.
- Mineral Sulfur: Effective for rosacea linked to Demodex mites, sulfur’s antifungal, antibacterial, and anti-parasitic properties can reduce mite populations and alleviate symptoms.
- Azelaic Acid: Studies show that azelaic acid 15% gel effectively reduces redness and inflammation in mild-to-moderate rosacea cases. It can also be combined with sulfur and niacinamide for enhanced results.
- Pink Clay Masks: Pink clay masks used once or twice a week can help reduce redness, improve skin texture, and absorb excess oil. They are a great addition to a rosacea-friendly skincare routine.
Oral Treatments
- Antibiotics: Oral antibiotics like minocycline can help reduce inflammation and target acne-causing bacteria in rosacea.
- Oral Supplements: Certain vitamins and minerals can help reduce redness and manage symptoms. For a detailed guide, click here.
- Laser and IPL Treatments: Laser or Intense Pulsed Light (IPL) therapy targets visible blood vessels and reduces redness. However, these treatments are typically ineffective for rosacea papules and pustules.
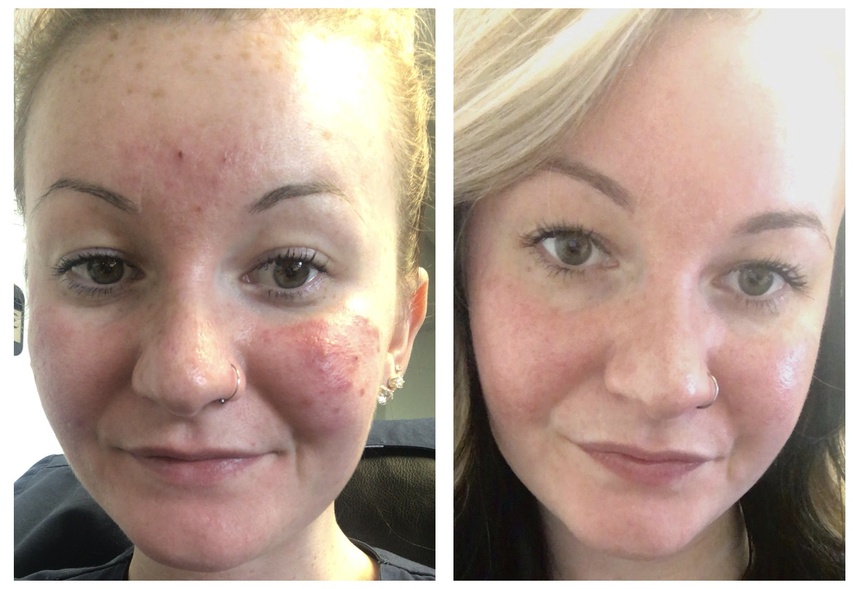

Rosacea- Before and After - MDacne customized acne treatment kit.
Preventing Rosacea Flare-Ups
Sun Protection: Rosacea-prone skin is highly sensitive to the sun, so applying sunscreen is crucial. Opt for light, oil-free chemical sunscreens with SPF 30, as higher SPF levels can sometimes be irritating.

Foods to Avoid for Rosacea Management
Diet plays an important role in managing rosacea symptoms. In a study by the National Rosacea Society, 95% of participants who improved their diets reported fewer breakouts. Avoid the following foods:
- Spicy Foods
- Alcohol (particularly red wine)
- Citrus Fruits
- Tomatoes and Eggplant
- Dairy Products
- Chocolate
- Soy Products
- Cinnamon and Nutmeg
By understanding the triggers and treatments for rosacea, you can better manage this condition and maintain clearer, healthier skin. While rosacea is a lifelong condition, a thoughtful skincare routine, and lifestyle adjustments can significantly reduce its impact.
Best vitamins and minerals for people with Rosacea and Rosacea-prone skin.
MDacne's sulfur+Niacinamaide+ azelaic acid treatment cream
Azelaic 10% Gel
References:
- Topical application of 1-methyl nicotinamide in the treatment of rosacea: a pilot study
- Botanicals and anti-inflammatories: natural ingredients for rosacea
- Update on the management of Rosacea
- A pilot study of 5 percent permethrin cream versus 0.75 percent metronidazole gel in acne rosacea
- Diet and rosacea: the role of dietary change in rosacea management
- Oral zinc sulfate in the treatment of rosacea: a double-blind, placebo-controlled study
- Incidence and prevalence of rosacea: a systematic review and meta-analysis.
To find the right acne treatments for your unique skin, take the free skin assessment by clicking here.