Everything you need to know about post-inflammatory erythema
Tackling Post-Inflammatory Erythema (PIE): Causes, Treatments, and Prevention
The battle with acne often doesn’t end once blemishes heal. Many people are left with pink, red, or even purple patches on the skin—known as post-inflammatory erythema (PIE). While not harmful, PIE can linger for months or even years if untreated.
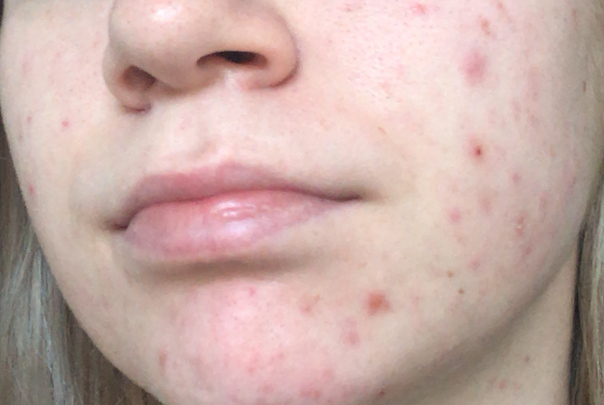
What is Post-Inflammatory Erythema (PIE)?
First coined in 2013, PIE refers to the residual pink or red discoloration left behind after inflammatory acne heals. It primarily affects individuals with lighter skin tones. PIE occurs due to inflammation, dilation, or damage to capillaries beneath the skin's surface, often caused by cystic acne but can also result from dermatitis, sun exposure, hormonal changes, aging, or skin injuries.
How to Treat Post-Inflammatory Erythema
Though PIE can fade naturally over time, treatments can expedite the healing process and minimize its appearance.
Topical Treatments
- Peptides and Ceramides: Products like the MDacne Peptide Scar Cream speed up healing, reduce inflammation, and strengthen the skin barrier.
- Niacinamide: This form of vitamin B3 reduces inflammation, strengthens the skin barrier, and minimizes redness. MDacne's Active Moisturizer with 4% niacinamide can also reduce pore size, balance oil production, and calm the skin.
- Hydrocortisone: A dermatologist-supervised option to reduce inflammation in persistent cases.
- Vitamin C: Brightens the skin, reduces redness, and strengthens capillary walls to address discoloration.
- Retinoids: Derived from vitamin A, retinoids fade scars, accelerate cell turnover and smooth skin texture.
Medical Treatments
- Laser Therapy: Options like pulsed dye lasers or intense pulsed light target damaged capillaries, reducing discoloration and inflammation. These treatments are also effective for rosacea and other vascular conditions.
- Microneedling: This procedure uses tiny needles to stimulate collagen production, improve skin texture, and reduce surface discoloration.
Preventing Post-Inflammatory Erythema
Prevention is easier than treatment. Incorporate these steps into your routine to reduce the risk of developing PIE:
- Avoid Picking or Popping Pimples: Picking spreads bacteria and increases inflammation, raising the chances of broken capillaries and PIE.
- Daily Sunscreen Use: Apply SPF 30 or higher to protect your skin from UV radiation, which can worsen inflammation and pigmentation.
- Establish a Consistent Skincare Routine: A targeted routine with anti-inflammatory and hydrating ingredients can resolve acne faster and prevent scars.
Active Ingredients for Prevention
- Salicylic Acid: Deeply exfoliates to unclog pores, reduce bacteria, and calm red, irritated skin.
- Benzoyl Peroxide: Antimicrobial properties help prevent breakouts and clear blocked pores. Available OTC or through prescription.
By addressing PIE through prevention, topical treatments, or professional care, you can achieve smoother, more even-toned skin. Explore options like MDacne's Peptide Scar Cream or Active Moisturizer in the MDacne shop to start your journey toward healthier skin.
References
- Flattening of atrophic acne scars by using tretinoin by iontophoresis
- Easy as PIE (Postinflammatory Erythema)
- Postinflammatory hyperpigmentation: a review of the epidemiology, clinical features, and treatment options in skin of color
To find the right acne treatments for your unique skin, take the free skin assessment by clicking here.



