Arbutin - the best hydroquinone-free dark spot remover

Key Points
- Arbutin is a gentle, plant-derived ingredient that effectively fades dark spots without irritating sensitive or darker skin tones.
- It works by slowly releasing hydroquinone and inhibiting tyrosinase, reducing melanin production and promoting an even complexion.
- Combining arbutin with exfoliants, retinol, and sunscreen enhances its efficacy for treating post-acne marks, melasma, and sun-induced pigmentation.
Understanding and Treating Dark Spots with Arbutin
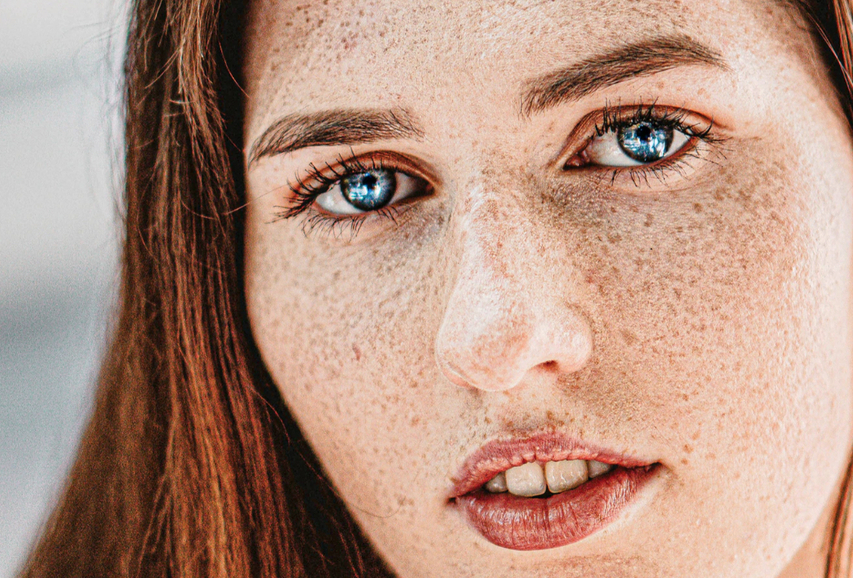
Dark spots, or hyperpigmented spots, are a top skin concern for many individuals and are often considered more bothersome than wrinkles. They result from excess melanin accumulation and can stem from various causes.
What Causes Dark Spots?
- Post-Inflammatory Hyperpigmentation (PIH): Caused by healed skin lesions like acne or eczema.
- Sun Exposure: Prolonged exposure to UV rays triggers melanin production, leading to spots.
- Hormonal Changes: Conditions like melasma are influenced by hormonal fluctuations.
How to Fade Dark Spots
To effectively fade dark spots, first address the underlying cause. For acne-related spots, control active breakouts. If caused by sun exposure, adopt daily use of an oil-free sunscreen. Once the trigger is managed, incorporate a dark spot remover to lighten pigmentation.
Choosing the Right Dark Spot Remover
- Hydroquinone-Based Products: These contain 2% Hydroquinone, retinoids, and anti-inflammatory agents. They are highly effective but may require a prescription outside the USA.
- Arbutin-Based Products: Derived from plants, Arbutin is a gentler alternative to Hydroquinone, offering gradual melanin reduction. Combined with retinol, AHAs, and BHAs, it effectively treats dark spots and uneven skin tones.
Why Choose Arbutin?
Arbutin, found in plants like barberry and blueberry, is a precursor to Hydroquinone. When applied to the skin, it releases Hydroquinone slowly, minimizing irritation while reducing melanin production. It also inhibits tyrosinase, the enzyme responsible for excess melanin, ensuring brighter, more even skin.
Key Benefits:
- Reduces sun-induced darkening.
- Safe for all skin types, including sensitive and darker skin tones.
- It does not increase sun sensitivity; it can be used year-round.
- Combines well with other ingredients like retinol, vitamin C, and niacinamide.
- Milder and safer than Hydroquinone.
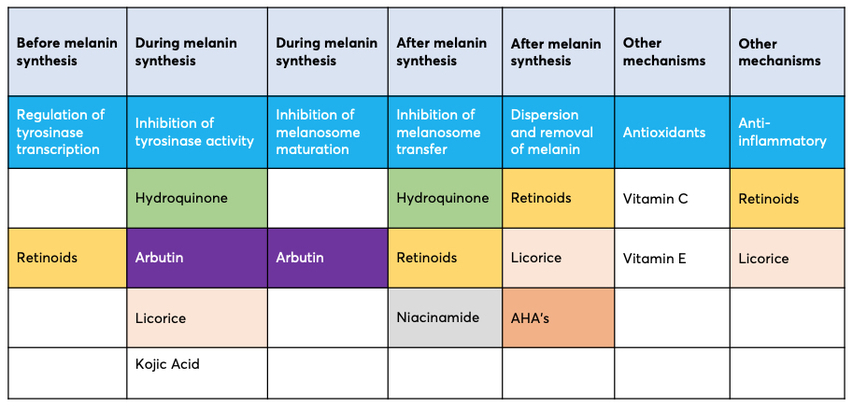
How to Use Arbutin
Apply Arbutin-based products, like the MDacne Advanced Dark Spot Remover, once daily in the evening after cleansing. For optimal results, pair with a broad-spectrum SPF 30 sunscreen during the day.
Enhancing Efficacy with Complementary Ingredients
The best formulations combine:
- Exfoliants: Glycolic and salicylic acids to enhance Arbutin penetration.
- Anti-Inflammatories: Bisabolol to reduce redness.
- Brightening Agents: Vitamin C, bearberry, and niacinamide for synergistic effects.
By incorporating Arbutin into your skincare routine, you can achieve a brighter, more even skin tone while gently and effectively fading dark spots.
Shop:
Arbutine based - Advanced Dark Spot Remover
Peptide Scar Cream
EltaMD UV Daily Tinted Sunscreen with Zinc Oxide, SPF 40
More info:
Best Acne Scar Products - Creams Vs Gels
FAQs
Q1: What are dark spots?
A1: Hyperpigmented areas caused by melanin buildup due to PIH, sun exposure, or hormonal changes.
Q2: Can Arbutin be used on sensitive skin?
A2: Yes, it’s safe for all skin types and is particularly gentle due to its slow-release mechanism.
Q3: Does Arbutin make skin sun-sensitive?
A3: No, but using sunscreen enhances its effectiveness.
Q4: What makes Arbutin better than Hydroquinone?
A4: Arbutin is milder, safer, and doesn’t damage pigment-producing cells, making it ideal for prolonged use.
Q5: Can Arbutin fade acne scars?
A5: Yes, it’s effective at reducing acne scars and brightening the skin when paired with retinol and niacinamide.
References:
- Inhibitory effects of alpha-arbutin on melanin synthesis in cultured human melanoma cells and a three-dimensional human skin model. Biol Pharm Bull. 2004 Apr;27(4):510-4.
- Inhibitory effects of arbutin on melanin biosynthesis of alpha-melanocyte-stimulating hormone-induced hyperpigmentation in cultured brownish guinea pig skin tissues. Arch Pharm Res. 2009 Mar;32(3):367-73.
- The melanogenesis and mechanisms of skin-lightening agents–existing and new approaches. Int J Cosmet Sci. 2011 Jun;33(3):210-21.
To find the right acne treatments for your unique skin, take the free skin assessment by clicking here.



